Push-pull solenoids are electromagnetic devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. They are widely used in various applications, ranging from industrial machinery to consumer electronics. In this article, we will explore the working principle, construction, and applications of push-pull solenoids.
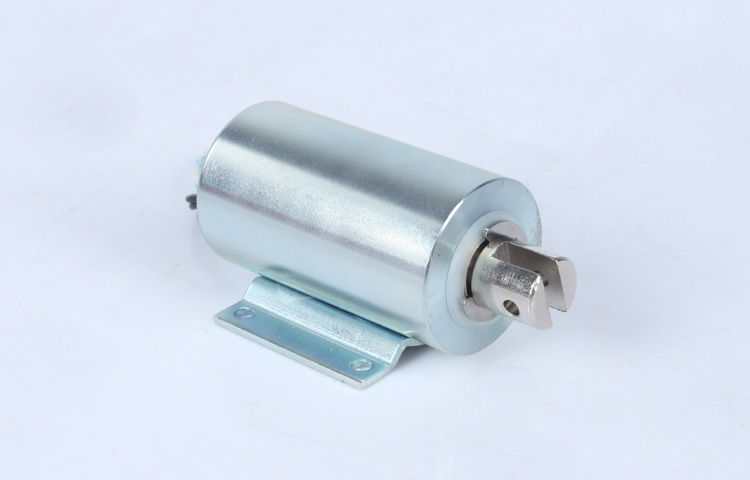

Working Principle
A push-pull solenoid consists of a coil of wire wound around a ferromagnetic core. When an electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field attracts a movable plunger or armature made of ferromagnetic material towards the solenoid’s core.
Construction
Push-pull solenoids typically have a cylindrical shape, with the coil wound around a central core. The core is usually made of a ferromagnetic material such as iron or steel, which enhances the magnetic field strength. The plunger or armature is attached to the core and moves back and forth when the solenoid is energized or de-energized.
Operation Modes
Push-pull solenoids can operate in two modes: push mode and pull mode.
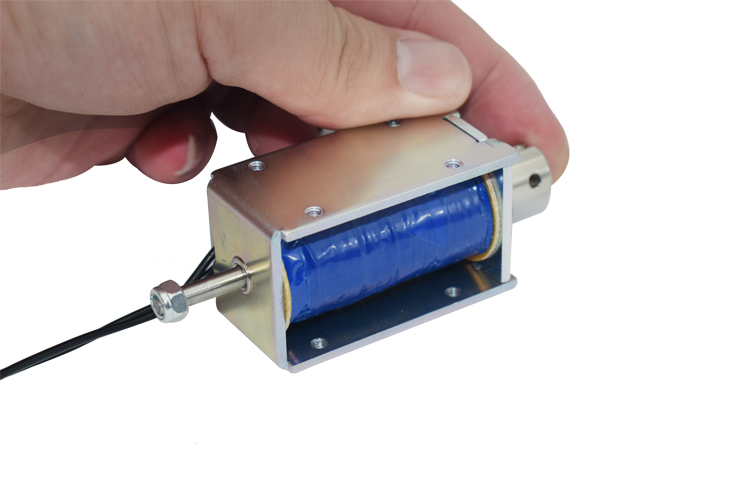
- Push Mode: In this mode, the solenoid is energized, and the magnetic field pulls the plunger towards the core, creating a pushing force. This mode is useful for applications that require pushing or actuating mechanisms, such as opening or closing doors, latches, or valves.
- Pull Mode: In this mode, the solenoid is de-energized, and a spring or other mechanical means pulls the plunger away from the core. This mode is useful for applications that require holding or locking mechanisms, such as locking doors or securing objects in place.
Applications
Push-pull solenoids find applications in various industries and devices due to their versatility. Here are a few examples:
- Automotive Industry: Push-pull solenoids are used in automotive applications, such as door locks, trunk latches, and fuel injectors.
- Industrial Machinery: They are employed in industrial machinery for tasks like actuating
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, push-pull solenoids are being further optimized for improved performance and efficiency. Manufacturers are developing solenoids with enhanced magnetic field strength, reduced power consumption, and increased durability to meet the evolving demands of various industries.
When incorporating push-pull solenoids into a design, it is essential to consider factors such as voltage requirements, stroke length, force output, and response time. Consulting with solenoid manufacturers or experts in the field can provide valuable insights and guidance for selecting the most suitable solenoid for a specific application.
In conclusion, push-pull solenoids play a crucial role in numerous electromechanical systems, offering reliable and efficient actuation capabilities. Their ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion makes them indispensable in various industries, from automotive and industrial machinery to medical equipment and consumer electronics. By understanding their working principles and applications, engineers and designers can harness the power of push-pull solenoids to create innovative and efficient solutions for a wide range of challenges.
